EtherChannel Link Aggregation Configuration on Cisco Router
This is detailed article on EtherChannel Link Aggregation Configuration on Cisco Router, as well as the verification and troubleshooting of link aggregation with EtherChannel.EtherChannel Configuration on Cisco
The following guidelines and restrictions are useful for configuring EtherChannel:
- EtherChannel support : all Ethernet interfaces on all modules must support EtherChannel, without the need for the interfaces to be physically contiguous or on the same module.
- Speed and duplex : Configure all interfaces in an EtherChannel to operate at the same speed and in the same duplex mode, as shown in the illustration.
- VLAN Matching : All interfaces in the EtherChannel group must be assigned to the same VLAN or configured as a trunk, which is also shown in the illustration.
- VLAN Range : An EtherChannel supports the same allowed VLAN range on all interfaces of a
- EtherChannel trunk. If the allowed VLAN range is not the same, the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel, even if they are set to automatic or desired mode.
After configuring the port channel interface, any configuration that applies to this interface also affects the individual interfaces. However, the settings that apply to individual interfaces do not affect the port channel interface. Therefore, making configuration changes to an interface that is part of an EtherChannel link can cause interface compatibility problems .
Interface configuration
The configuration of EtherChannel with LACP is done in two steps:- Step 1 . Specify the interfaces that make up the EtherChannel group using the interface range range interface command in global configuration mode. The range keyword allows you to select several interfaces and configure them at the same time. It is recommended to start by deactivating those interfaces, so that no incomplete configuration creates link activity.
- Step 2 . Create the port channel interface with the channel-group identifier mode active command in interface range configuration mode. The identifier specifies the channel group number. Mode active keywords identify this setting as EtherChannel LACP.
In Image 2, FastEthernet0 / 1 and FastEthernet0 / 2 are grouped in the EtherChannel 1 interface port channel.
To change the Layer 2 configuration in the port channel interface, enter the port channel interface configuration mode using the interface port-channel command , followed by the interface identifier.
In the example, the EtherChannel is configured as a trunk link interface with specific allowed VLANs. In Image 2, it is also shown that the interface port channel 1 is configured as a trunk link with the allowed VLANs 1, 2 and 20.
EtherChannel Verification
There are a variety of commands to verify an EtherChannel configuration .- First, the show interface port-channel command shows the general status of the port channel interface. In Image 3, the port channel interface 1 is active.
- When multiple port channel interfaces are configured on the same device, use the show etherchannel summary command to display a single line of information per port channel. In Image 4, the switch has an EtherChannel configured; Group 1 uses LACP.
The interface group consists of the FastEthernet0 / 1 and FastEthernet0 / 2 interfaces. The group is a Layer 2 EtherChannel and is in use, as indicated by the letters SU next to the port channel number.
- Use the show etherchannel port-channel command to display information about a specific port channel interface, as shown in Image 5.
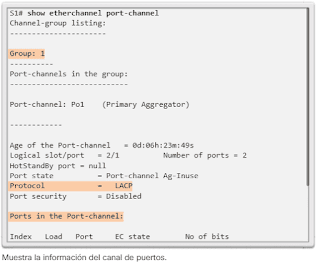
In the example, the port channel interface 1 consists of two physical interfaces, FastEthernet0 / 1 and FastEthernet0 / 2. It uses LACP in active mode. It is correctly connected to another switch with a compatible configuration, which is why it is said that the port channel is in use.
In any member of a physical interface of an EtherChannel group, the show interfaces etherchannel command can provide information about the function of the interface in the EtherChannel, as shown in following figure.
The FastEthernet0 / 1 interface is part of the EtherChannel 1 group. The protocol for this EtherChannel is LACP.
EtherChannel troubleshooting
All interfaces within an EtherChannel must have the same speed and duplex mode settings, native and allowed VLANs on trunk links, and access VLANs on access ports.- Assign all ports on the EtherChannel to the same VLAN or configure them as a trunk. Ports with different native VLANs cannot form an EtherChannel.
- When configuring an EtherChannel from trunk links, verify that the trunk mode is the same on all trunk links . Inconsistent trunk link modes on the EtherChannel ports can cause EtherChannel to not work and the ports to be disabled (errdisable state).
- An EtherChannel supports the same allowed VLAN range on all ports . If the allowed VLAN range is not the same, the ports do not form an EtherChannel, even when PAgP is set to automatic or desirable mode.
- Dynamic negotiation options for PAgP and LACP must be configured in a compatible manner at both ends of the EtherChannel.
Note : it is easy to confuse PAgP or LACP with DTP, since both are protocols that are used to automate the behavior on trunks. PAgP and LACP are used for link aggregation (EtherChannel). DTP is used to automate the creation of trunks. When an EtherChannel trunk is configured, EtherChannel (PAgP or LACP) is usually configured first and then DTP.
Result Examples
In Image 7, the F0 / 1 and F0 / 2 interfaces on switches S1 and S2 are connected to an EtherChannel. The result indicates that the EtherChannel is inactive.In Image 8, a more detailed result indicates that there are incompatible PAgP modes configured on switches S1 and S2.
EtherChannel 2 troubleshooting
Image 8: incompatible PAgP modes
In Image 9, the PAgP mode in the EtherChannel is changed to desired, and the EtherChannel is activated.
If you try to change the configuration directly, the errors in the expansion tree cause the associated ports to enter the blocking or errdisabled state .







No comments:
Post a Comment