Advanced Single-Area OSPF Configurations On Cisco Router
OSPF is a popular link state routing protocol that can be adjusted in many ways. here you will learn Advanced Single-Area OSPF Configurations On Cisco Router. Some of the most common tuning methods include the manipulation of the process of choice of the designated router / designated backup router (DR / BDR), the propagation of predetermined routes, the adjustment of the OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 interfaces and the authentication enable.What is Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
OSPF is a link state routing protocol that is frequently implemented and developed as a replacement for the RIP distance vector routing protocol . However, OSPF has significant advantages compared to RIP, as it offers faster convergence and scale to much larger network implementations.OSPF features:
- Classless : was conceived as a classless protocol, so that supports VLSM and CIDR.
- Effective : routing changes trigger routing updates (no periodic updates). Use the SPF algorithm to choose the best route.
- Fast convergence : quickly propagates the changes that are made to the network.
- Scalable : works well in small and large networks. Routers can be grouped into areas to support a hierarchical system.
- Secure : Supports the synthesis of message 5 (MD5) synthesis. When enabled, OSPF routers only accept encrypted routing updates from peers with the same password previously shared.
OSPF single Area Configuration on Cisco
This chapter focuses on adjustments and troubleshooting OSPF . However, it is recommended to review a basic implementation of the OSPF routing protocol.The example in figure shows the topology used to configure OSPFv2.
The routers in the topology have an initial configuration, which includes interface addresses enabled. At this time, none of the routers have static routing or dynamic routing configured. All interfaces on routers R1, R2 and R3 (except the loopback interface on R2) are within the OSPF backbone area. The ISP router is used as the gateway of the routing domain to the Internet.
In Image 4, the Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 interface of R1 is configured to reflect its actual bandwidth of 1 000 000 kilobits (ie 1 000 000 000 b / s).
Then in the OSPF router configuration mode, the router ID is assigned, the reference bandwidth for the fast interfaces is set and the three networks connected to R1 are announced. Notice how the wildcard mask is used to identify specific networks.
In figure, the Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 interface of the R2 is also configured to reflect its actual bandwidth, the router ID is assigned, the reference bandwidth is set for the fast interfaces and the three networks are announced connected to R2.
Note the way in which the use of the wildcard mask can be avoided by identifying the router interface itself with a zero quad mask. This causes OSPF to use the subnet mask assigned to the router interface as the advertised network mask.
OSPF verification of single area
Some of the useful commands for verifying OSPF are the following (the result corresponding to each verification command that was entered in R1 is shown.):- show ip ospf neighbor : command to verify that the router formed an adjacency with neighboring routers. If the neighbor router ID is not displayed or is not shown in the FULL state, the two routers did not form an OSPF adjacency.
- show ip protocols : command that provides a quick way to verify fundamental OSPF configuration information. This includes the OSPF process ID, the router ID, the networks announced by the router, the neighbors from which the router receives updates, and the default administrative distance, which for OSPF is 110.
- show ip ospf : command used to display the OSPF process ID and router ID, as well as the OSPF SPF and OSPF area information.
- show ip ospf interface : command that provides a detailed list of each interface with OSPF enabled and is very useful to determine if the network instructions were composed correctly.
- show ip ospf interface brief : useful command to show a summary and the status of interfaces with OSPF enabled.
Configuration of OSPFv3 single area
The following is a review of a basic implementation of the OSPFv3 routing protocol for IPv6.In the example the topology used to configure OSPFv3 is shown.
The routers in the topology have an initial configuration, which includes IPv6 interface addresses enabled. At this time, none of the routers have static routing or dynamic routing configured. All interfaces on routers R1, R2 and R3 (except the loopback interface on R2) are within the OSPF backbone area.
In Image , in the configuration mode of the OSPFv3 router of R1, the router ID is assigned manually and the reference bandwidth is set for fast interfaces. Next, the interfaces that participate in OSPFv3 are configured. The Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 interface is also configured to reflect its actual bandwidth.
Note that, when OSPFv3 is configured, a wildcard mask is not required.
In Image , in the configuration mode of the OSPFv3 router of R2, the router ID is assigned manually and the reference bandwidth is set for fast interfaces. Next, the interfaces that participate in OSPFv3 are configured. The Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 interface is also configured here to reflect its actual bandwidth.
Verification of single area OSPFv3
Finally, some of the useful commands for verifying OSPFv3 are the following: (the result corresponding to each verification command that was entered in R1 is shown.)- show ipv6 ospf neighbor : command to verify that the router formed an adjacency with neighboring routers. If the neighbor router ID is not displayed or is not shown in the FULL state, the two routers did not form an OSPF adjacency.
- show ipv6 protocols : this command provides a quick way to verify fundamental OSPFv3 configuration information, including the OSPF process ID, router ID and OSPFv3 enabled interfaces.
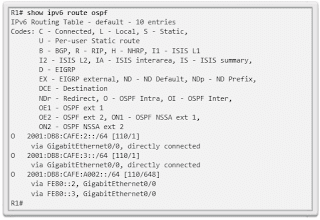
- show ipv6 route ospf : this command provides specific data about OSPFv3 routes in the routing table.
show ipv6 ospf interface brief : useful command to show a summary and the status of interfaces with OSPFv3 enabled.














No comments:
Post a Comment